Triple-combination CAB gel effective, well-tolerated in all age groups
Today's report also covers acne scarring, reducing sebum production, dry eye symptoms, and more (1,800 words, 7 minutes, 30 seconds)
The Focus on Acne e-newsletter is supported by an unrestricted grant from Sun Pharma Canada
Good morning, and welcome to the 20th issue of Focus on Acne, presented by Skin Spectrum Weekly. This series provides up-to-date information on developing therapies and trends in acne treatment. We appreciate your feedback and suggestions and invite you to be in touch. Please write to us at health@chronicle.org
Triple-combination CAB gel effective, well-tolerated in all age groups
Findings from a recent study show a fixed-dose, triple-combination clindamycin phosphate 1.2%/adapalene 0.15%/benzoyl peroxide 3.1% (CAB) gel was efficacious and well-tolerated in participants with moderate-to-severe acne, regardless of age. Approximately one-half of the participants achieved clear or almost clear skin, with reductions of greater than 70% in lesion counts.
The findings were published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (2025 Dec. 1; 24(12):1186-1194).
In one phase 2 (NCT03170388) and two phase 3 (NCT04214652, NCT04214639) trials, researchers randomized participants nine years of age or older with moderate-to-severe acne to once-daily CAB or vehicle gel.
Investigators analyzed pooled data grouped by age: younger (9-24 years; n=515) and adult (=>25 years; n=142). Endpoints included the percentage of participants achieving treatment success (a greater than or equal to 2-grade reduction from baseline in the Evaluator’s Global Severity Score and clear/almost clear skin) and the least-squares mean per cent change from baseline in inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions at week 12.
Researchers evaluated treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) throughout the study.
At week 12, approximately one-half of CAB-treated participants in both age groups achieved treatment success (9-24: 50.6%; greater than or equal to 25: 49.0%) vs less than one-fourth with vehicle (15.7%; 20.6%; p<0.01 for both). Across groups, CAB yielded >70% reductions in inflammatory/noninflammatory lesions vs 45% to 62% with vehicle (p<=0.001 for all). For all endpoints, CAB efficacy was similar across age groups. Most TEAEs with CAB were of mild-to-moderate severity, and there were no age-related trends in safety/tolerability.
Psychological journey of patients with acne scarring clarified
Patients with atrophic acne scarring experience a four-stage psychological journey with uncertainty about their illness persistently impacting their psychological and social functioning, researchers report in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology (2025 Nov. 28; 18:3223-3238).
Investigators conducted the study to explore the psychological experiences of patients with atrophic acne scarring during the disease progression and analyze their emotional changes and coping strategies based on uncertainty in illness theory.
The authors selected 15 patients with atrophic acne scarring from a tertiary hospital in Henan Province, China. They conducted semi-structured, in-depth interviews with the patients.
From the survey data, researchers identified four themes and 12 sub-themes, including:
1) Confusion and denial in the initial diagnosis stage (including disease-related cognitive bias, information confusion and incorrect interventions, and a normalization tendency).
2) Anxiety and shame in the flare stage (including appearance monitoring behaviours, social evaluation pressure, and impaired social functioning).
3) Coping strategies in the long-term adaptation stage (encompassing positive coping, negative coping, and polarized adaptation patterns).
4) Psychological adjustment in the recovery stage (patients experienced contradictory acceptance, post-traumatic growth, and behavioural-psychological asynchronous improvement).
Uncertainty about illness persisted throughout the process, affecting patients’ self-recognition, social behaviours, and treatment adherence.
The authors conclude healthcare providers should offer personalized psychological support based on the framework of uncertainty in illness theory to enhance patients’ quality of life.
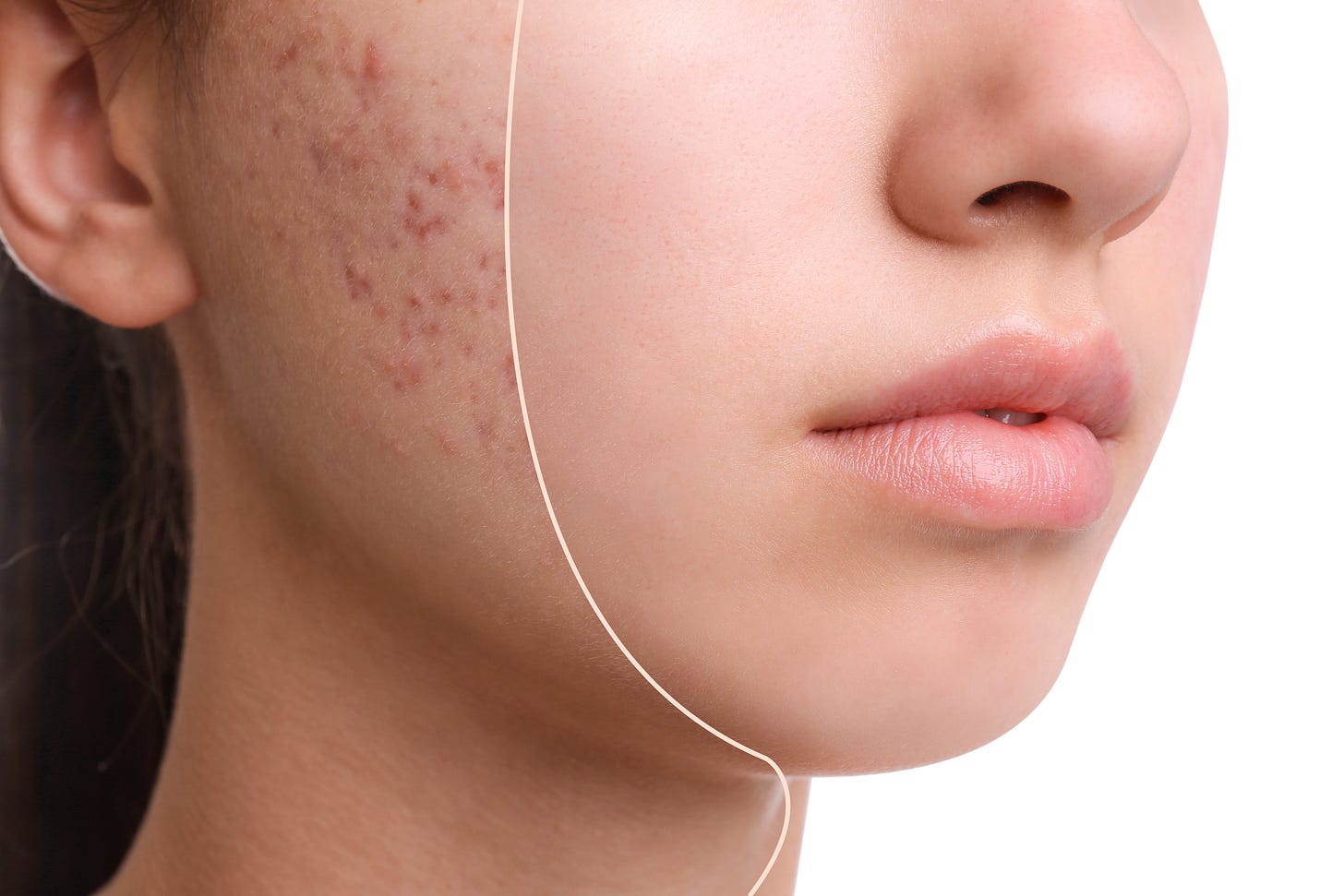

Topical clascoterone cream 1% significantly reduces sebum production
A study measuring reductions in casual sebum production in patients with acne following 12 weeks of treatment with clascoterone cream 1% has found treatment led to significant reductions in sebum measurements with improvements in acne severity. The treatment was also well tolerated.
The study was published in Dermatology and Therapy (2025 Sept.; 15(9):2657-2666).
For this study, patients aged 12 years or older with mild-to-moderate acne applied clascoterone cream 1% twice daily for 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was the reduction in casual sebum measurements at Week 12. Additional endpoints included Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) score, inflammatory and noninflammatory lesion counts (ILC and NILC), and tolerability.
In total, researchers enrolled 40 patients with a mean age of 20.9 years, all of whom completed Week 12. Investigators observed significant percentage reductions from baseline in sebum measurements (27%), ILC (54%), and NILC (34%; all p<0.001), and patients achieved a 29% reduction in IGA score. The authors identified no tolerability or safety issues during the 12-week interim analysis period.
Link between isotretinoin therapy for acne and dry eye symptoms evaluated
Isotretinoin therapy in patients with acne vulgaris (AV) is remarkably associated with greater meibomian gland loss (MGL), severe dry eye symptoms, and reduced tear film stability, according to new findings. This discovery supports a lipid-deficient mechanism in isotretinoin-induced dry eye disease (DED).
These findings were published in The Medical Journal of Malaysia (2025 Nov.; 80(6):780-786).
Researchers conducted a comparative cross-sectional observational study at two tertiary hospitals between Aug. 2022 and May 2023. They recruited 48 patients with AV and categorized them into isotretinoin-treated (n=19) and isotretinoin-naive (n=29) groups. Investigators used a LacryDiag® ocular surface analyzer to evaluate meibomian gland loss (MGL) and tear film parameters. They also administered the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) questionnaire to evaluate dry eye symptoms, severity, and functional effects.
At enrollment, the mean duration of AV was 5.26±3.28 and 6.39±5.63 years in the treated and naive groups, respectively. Treated participants had completed a minimum of 16 weeks of daily isotretinoin therapy at the time of examination (mean: 16.89±3.2 weeks). The OSDI score was markedly higher in the treated group than in the naive group (43.20±18.79 vs 18.15±19.24). The isotretinoin-treated group had a significantly greater MGL percentage than the naive group (p<0.001), significantly lower noninvasive break-up time (NIBUT) (p=0.046) and lipid layer thickness (p<0.001). The mean tear meniscus height was also lower in the treated group, although the difference was not statistically significant (p=0.462). Pearson’s correlation analysis revealed a significantly moderate positive correlation between the MGL percentage and the OSDI score (r=0.417, p=0.003) and a significantly moderate negative correlation between the MGL percentage and the NIBUT (r=-0.348, p=0.015).
In their conclusions, the researchers recommend routine ocular surface evaluations to detect and manage ocular complications in patients receiving isotretinoin.
Subscribe to The Chronicle of Skin & Allergy
Established in 1995, The Chronicle of Skin & Allergy is a scientific newspaper providing news and information on practical therapeutics and clinical progress in dermatologic medicine.
To apply for a complimentary* subscription, please email health@chronicle.org with your contact information or click the link below.
If you find the contents of this newsletter interesting, please check out the Yadav on Acne podcast. It’s available at Apple iTunes, Stitcher, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts.